 |
This option is used to maintain the database environment, their tables and objects as related to the ITS system.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
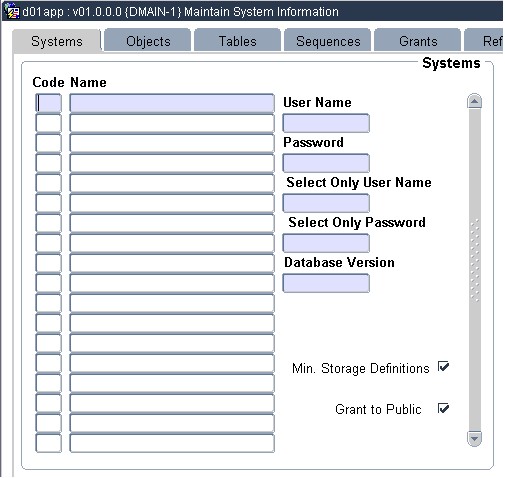
| System Code | A1 | A unique code assigned to every system. |
| Name | A30 | The name of the system. |
| User Name | A10 | The Oracle Username under which the tables are created. This Schema is the owner of the tables. |
| Password | A10 | The Oracle password of the username creating the tables. Passwords will be displayed using asterisks. |
| DB Version | A2 | The current version of the Oracle database on this
computer. |
| Select User Name | A10 | For every system, a select username must be created in
Oracle using the
GRANT verb in SQL*Plus. Only connect privileges must be given
to this
user. For every table created by the owner, a grant select to
the
select user is inserted when the definition file is generated in option
{DMAIN-2}. It
is essential to note that these passwords are only used
for the generation of data definition scripts. They are not for
system functionaltity. |
| Select Password | A10 | The password of the select username. |
| Min. Storage Definition | Tick Box | The question asked is whether the storage parameters
used, when
generating the definition file {DMAIN-2}, must be as specified in Block
4 of this program, or whether a default minimum should be
used.
Normally one would decide on the storage parameters when designing a
system. Tables with large volumes of data will have large
storage
parameters so as to prevent the creation of extents. It is sometimes necessary to create tables for a system, which is not being used, in order to facilitate integration. The large tables in such a system will use a large amount of space in Oracle without ever inserting that amount of data. In such cases this parameter can be set to (Y)es, which will not generate the large storage parameters. |
| Grants to Public | Tick Box |
The system will not create grants to public anymore. All these grants will be revoked and replaced with grants to the valid ITS systems. There are, however, systems (i.e. WEB) that should have limited access to tables or views of other systems. For these, one should set this value to “N”. |
|
For every system, a number
of sub-system can be created. All tables linked to the same
system must use the same Oracle username, but every sub-system can have
a data definition file.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| System Code | A1 | As defined in option {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems. |
| sub-system Code | A1 | A code that must be unique within a system. |
| sub-system Name | A30 | The name by which the sub-system will be known. |
| Data Definition File Name for Tables and Sequences | A30 | When the data definition file for this sub-system is generated in {DMAIN-2}, this UNIX file name will be used. The name can be relative or absolute. |
| Headings File Name | A30 | When the SQL*Plus heading and format file is generated for this sub-system in {DMAIN-3}, this file name will be used. |
| Data Definition File Name for Views | A30 | When the view data definition file for this sub-system is generated in {DMAIN-2}, this UNIX file name will be used. The name can be relative or absolute. There is currently only one file per system. |
| Local Software | Tick Box | Is this sub-system local software to this institution? Some reports require this information to generate definition files. |
|
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tablespace Code | A6 | Code of the table space as used in Oracle. |
| Name | A30 | Description of the table space. |
|
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| System Code | A1 | As defined in {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems. |
| Definition Code | A6 | It is not necessary to create a storage definition for
every table. A
number of standard definitions can be created within a system and then
linked to a table or index via this code. This code must be
unique
within a system. |
| Name | A30 | The name of the storage definition. |
| Data Initial | N6 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| Data Increment | N6 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| Data Max Extents | N6 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| % Free | N2 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| Index Initial | N6 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| Index Increment | N6 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| Index Max Extents | N6 | The user is referred to the Oracle Manual where storage parameters are discussed. |
| Tablespace | A6 | The tablespace in which a table will be created when it is linked to this storage definition. Tablespaces for the creation of indexes are specified in {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems: Table Space |
|
For every system a number
of sub-system can be created. All tables linked to the same
system must use the same Oracle username, but every sub-system can have
a data definition file.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table Id | A4 | This Id is the unique identifier of a
table/view. All references to a table in this system are made
to this Id. |
| Table Code | A3 | The Oracle table name is made by concatenating the Table Id and the Table Code, e.g. a Table Id of “IAD” and a Table Code of “BIO” will result in an Oracle table IADBIO being created. The Column name in a table will always start with the Table Id, followed by the Object name {DMAIN-1b7}. This field must not be entered ifthe table is to be a sequence or a view (refer to C. below). |
| System Code | A1 | As defined in {DMAIN-1), TAB - Systems: Sub system. |
| Sub-system Code | A1 | As defined in {DMAIN-1), TAB - Systems: Sub system. This must be left blank for views. |
| Storage Definition | A6 | As defined in {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems: Storage Definition. This storage
definition and the resulting
storage parameters will be used to create the data table, unless the
minimum system specification in {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems is set to (Y)es.
This must
be left blank for views. |
| Table Name | A30 | A short name describing the use of the
table/view. For sequences and views this will be the name
used in the Oracle Database. |
| Number of Columns/Line | N1 | When the data definition file is generated, tables/views with many columns could become a long narrow list. To allow for more than 1 column definition per line, set this parameter to a value greater than 1. |
| Log Table ID | A4 | The table prefix for the log table, which is triggered by
a database
trigger, should be created in order to log all changes to it. Please note
that all
changes to the data in this table will be logged. Upon
entering the
table prefix, the name and description will be displayed. |
| Table/Sequence/View | A1 | This indicates, whether this definition is for a Table, View or Sequence. |
| Table Description | A80 | A more comprehensive description of the use of the table / view. |
| On This Computer? | A1 | Application systems can be distributed over more than one computer system. The definition of the table / view is needed in this system, but database administration functions cannot be performed on these tables as they do not exist on this computer. A (N)o will indicate that programs generating code for database administration functions will ignore these tables. |
| Date Released | DD-MON-YYYY | The date on which this table / view became part of the
system. |
| Discontinued | DD-MON-YYYY | The date on which this table / view was discontinued from
the system. No
database administration functions will be performed on tables with a
date entered here. |
| Include in Data Model | A1 | Must the table be included in the data model
definition? There may be
numerous small or temporary tables used for sorting that one does not
want in the data model. These just seem to clutter up the
picture and
may be excluded. |
| Is this a code structure Table | A1 | An indication of whether this table is used for a code
structure defining an object or being used in a lookup function. |
|
Any system integration
grants can be specified here. The generation of the data
definition file {DMAIN-2}
will insert the grant specified here as well as the grant to the select
user, as defined in option {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems. More than one grant
can be specified per table. Grants to Public may be defined
here: but in the actual generated definitions file grants will be given to all the ITS systems individually.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table ID | A4 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b5} |
| Permission | A1 | The type of permission to be granted: allowed values
are:
|
| Grant | A1 | A (Y)es will add the
“WITH GRANT OPTION” to the grant statement. |
| Public | A1 | A (Y)es will
generate a “grant all” to the
ITS systems as defined in Block 1 - with the “Grants Y/N for
public set to “Y”. |
| Grant to | A1 | If the grant
is not to public, a system code {DMAIN-1}, TAB - Systems can be entered here and the
grant will only be inserted to the specified system. |
|
This is the central list
of all database objects. The concept is to define all the
objects of all systems only once in this Block and then to link it to
different tables.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Object Code | A4 | This unique object code identifies the
object. All references to the object are made via this object
code. |
| Name | A30 | The name of the object. The table Id
{DMAIN-1b5} will be concatenated to this object name to form the column
name in every table. |
| Type | A1 | Object type: allowed values are:
|
| Print Format | A20 | This format will be used when the heading and format
file is generated
{DMAIN-3}. This format must be large enough to cover the
space needed
for the Print Heading in the same block. |
| Width | N3 | The width of this object, including the scale portion. |
| Date Format | DD-MON-YYYY | The date format of a date field. |
| Scale | N1 | The scale of this object: leave “0” for no scale. |
| Print Heading line 1 and 2 | A30 x 2 | This heading will be used when generating the heading and format file {DMAIN-3}. Line 1 will be on top and line 2 underneath. This will also be used as the field names for view columns, separated by a “_” character. |
| Object Qualifier line 1 and 2 | A30 x 2 | This is a more descriptive heading for the object. |
| Definition of Object | A40 x 6 | 6 Lines to describe the usage and definition of the
object. This will be printed in the technical documentation {DMAIN-4}. |
| Date Created | DD-MON-YYYY | The date that this object was created or altered. |
|
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table ID | A4 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b5}. |
| Column Number | N4 | Order of this object within the table. |
| Object Code | A4 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b7}. |
| Allow Null Values | A1 | A (N)o will generate the phrase “NOT NULL” as part of the table definition. |
| Merge Calculation Method | A30 | This is used when different institutions do a merge
and their databases have to merge. |
| Is this a Code Structure Column | Y/N/A | Does this column refer to a code structure? |
| Synonym | A30 | Synonym of the object. |
| Remarks | A30 | Any remarks to further identify the usage of the object in the specific table can be entered here. |
| Date Released | DD-MON-YYYY | Date on which this object was linked to this table. |
| Discontinued | DD-MON-YYYY | Date from which this object was no longer used in this table. |
|
The existence of primary
keys and indexes are specified here. One primary key and
multiple search keys may be defined per table.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table Id | A4 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b5}. |
| Index Id | A10 | he Table Id concatenated to the Index Id forms the name of the index to be used in Oracle. |
| Name | A30 | Descriptive name of the index. |
| Unique | A1 | A (Y)es will add the phrase
“UNIQUE” to the CREATE INDEX statement. |
| Tablespace | A6 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b3}. The index will be
created in the specified table space. |
| Primary Key | A1 | A (Y)es will result in the index being created as a primary key in the database. |
| Created | DD-MON-YYYY | This date cannot be updated and defaults to system date
when the record is created, or when any changes are made to the index. |
|
In this Block the columns
of the table are linked to index definitions. More than one
column can be linked to an index.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table Id | A4 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b9}. |
| Index Id | A10 | As defined in {DMAIN-1b9}. |
| Column Number | N4 | As entered in the column definition in {DMAIN-1b8}. |
| Order | N2 | Order of this object within the index. |
|
All foreign key references
are specified here. For every table, a number of constraints
can be specified. For every table / constraint, more than one
field can be specified.
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Base Table Id | A4 | The Id of the base table. |
| Constraint Number | N2 | The number of the constraint within this base table. |
| Order | N2 | The sequence of this column within the foreign key. |
| Base Column | N4 | The column number of this field in the base
table. The field description will be displayed by the system. |
| Reference Table | A4 | The ID of the table this foreign key points to. |
| Reference Column | N4 | The column number of the field in the reference table. |
|
| Field | Type & Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table Code | A4 | The table code, as defined in the TABLES tab. The table description will be displayed. |
| Constraint Name | A10 | A valid Oracle name for the constraints. No spaces or special characters allowed (especially @ signs). |
| Constraint Detail | A2000 | Enter the Oracle commands to specify this constraint. |
|
| Processing Rules |
|
|---|---|
| No special processing rules. |
| Date | System Version | By Whom | Job | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08-Jan-2007 | v01.0.0.0 | Amanda Nell | t134411 | New manual format. |
| 12-Mar-2008 | v01.0.0.0 | Vaughn Dumas | t134411 | Add missing blocks, remove views, system owner proof read |
| 18-Sep-2008 | v01.0.0.0 | Charlene van der Schyff | t151648 | Edit language obtained from proof read language Juliet Gillies. |